What are the most common fertility treatments? Which is most suitable for me?
In order to achieve a pregnancy, the egg has to be fertilised by the sperm. Fertilisation is the fusion of an egg and a sperm to form an embryo. Fertilisation can occur in-vivo (inside body such as conceiving by natural means) or in-vitro (outside the body). Fertilisation that occurs outside the body is known as in-vitro fertilisation.
The most common fertility treatments are:
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in In-vitro Fertilisation (IVF) treatment
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) treatment
The difference between IVF and IUI is that in IVF, fertilisation occurs outside of the body, in a culture dish under controlled laboratory conditions. In IUI, fertilisation occurs inside of the body.
1. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
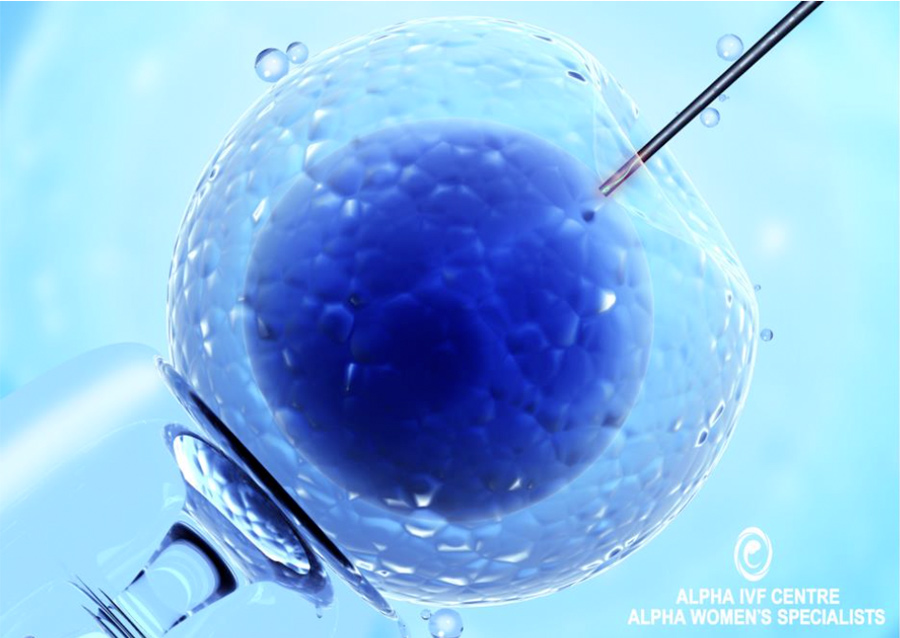
ICSI is a technique that injects a single sperm directly into an egg to assist with fertilisation. It bypasses the initial fertilisation process where the sperm no longer needs to penetrate the zona pellucida layer on its own. The zona pellucida layer is a thick layer of egg membrane commonly referred as the egg shell. In IVF treatments, fertilisation occurs outside of the body (in a lab dish).
2. Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)

IUI is a treatment that involves inserting the husband’s washed and concentrated sperm sample back into the wife’s uterus during ovulation to aid natural fertilisation.
What are the advantages of IVF and IUI treatments?
Advantages of IVF
ICSI helps to increase the chance of fertilisation if your partner has male factor issues. Male factor issues include poor sperm motility (the ability of the sperm to swim forward), poor sperm morphology (the shape and size of the sperm) and/or low sperm concentration. The chances of fertilisation increase as there is no need for the sperm to penetrate the egg shell to initiate fertilization.
At Alpha IVF Centre, we leverage on technologies such as pulse-driven ICSI, time lapse culture system, and artificial intelligence (AI) to increase the success rate. Study has shown that pulse-driven ICSI demonstrated a higher fertilisation rate compared to conventional ICSI method.
Advantages of IUI
IUI treatment is less costly compared to IVF as fewer fertility medications are used. It is a quick and simple procedure, that is performed according to the timing of natural ovulation. However, more than 1 insemination attempt may be needed to achieve pregnancy.
Are there any risks in fertility treatment?
1. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is a risk present during ovarian stimulation. OHSS occurs when there are too many ovarian follicles developing in response to hormones used to make eggs grow. OHSS can vary from mild to severe complications. Most cases of OHSS are mild, with symptoms such as abdominal bloatedness, nausea and vomiting. Although severe cases of OHSS may lead to serious illness or death, it is rare.
2. Multiple pregnancy through Super-Ovulation & Intrauterine Insemination (SO-IUI). Instead of naturally ovulating 1 egg at a time, SO-IUI increase the chances of conception as 2 to 3 ovarian follicles are stimulated and ovulated. This may result in multiple pregnancy if more than 1 egg fertilise.
3. There is no significant change in risk of major birth defects or abnormalities in children conceived through fertility treatment when compared with spontaneous conception.
References
[1] Wang, J., & Sauer, M. V. (2006). In vitro fertilization (IVF): A review of 3 decades of Clinical Innovation and Technological Advancement. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 2(4), 355–364. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.2006.2.4.355
[2] The importance of 3 full cycles of IVF. NICE. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.nice.org.uk/news/blog/the-importance-of-3-full-cycles-of-ivf.
[3] Schorsch, M., Gomez, R., Hahn, T., Hoelscher-Obermaier, J., Seufert, R., & Skala, C. (2013). Success rate of inseminations dependent on maternal age? an analysis of 4246 insemination cycles. Geburtshilfe Und Frauenheilkunde, 73(08), 808–811. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1350615